# 12.ns3 wifi 模块从 Socket 到 WifiNetDevice
在本节中,将从源码的角度解析 ns3 的 wifi 模块,包括一个 packet 是如何从一台主机的 Socket 到另一台主机的 Socket 。
PS:
本节很长,而且很枯燥,但是对扩展
ns3功能,了解ns3流程非常有帮助,请耐心观看。本节的源码来自于
ns3.32, 不同版本之间有一些差异,但大致流程差不多,可以互相参考。本节需要一定的前置知识,推荐先阅读上一节 11.ns3 wifi 模块流程源码解析,大致了解
Packet从NetDevice到物理层之间的调用过程
# 发送过程分析
Socket 通信必定离不开 Socket::Send 函数,所以今天我们的起点就是 Socket::Send
network/model/socket.h
/** | |
* \brief Send data (or dummy data) to the remote host | |
* | |
* This function matches closely in semantics to the send() function | |
* call in the standard C library (libc): | |
* ssize_t send (int s, const void *msg, size_t len, int flags); | |
* except that the send I/O is asynchronous. This is the | |
* primary Send method at this low-level API and must be implemented | |
* by subclasses. | |
* | |
* In a typical blocking sockets model, this call would block upon | |
* lack of space to hold the message to be sent. In ns-3 at this | |
* API, the call returns immediately in such a case, but the callback | |
* registered with SetSendCallback() is invoked when the socket | |
* has space (when it conceptually unblocks); this is an asynchronous | |
* I/O model for send(). | |
* | |
* This variant of Send() uses class ns3::Packet to encapsulate | |
* data, rather than providing a raw pointer and length field. | |
* This allows an ns-3 application to attach tags if desired (such | |
* as a flow ID) and may allow the simulator to avoid some data | |
* copies. Despite the appearance of sending Packets on a stream | |
* socket, just think of it as a fancy byte buffer with streaming | |
* semantics. | |
* | |
* If either the message buffer within the Packet is too long to pass | |
* atomically through the underlying protocol (for datagram sockets), | |
* or the message buffer cannot entirely fit in the transmit buffer | |
* (for stream sockets), -1 is returned and SocketErrno is set | |
* to ERROR_MSGSIZE. If the packet does not fit, the caller can | |
* split the Packet (based on information obtained from | |
* GetTxAvailable) and reattempt to send the data. | |
* | |
* The flags argument is formed by or'ing one or more of the values: | |
* MSG_OOB process out-of-band data | |
* MSG_DONTROUTE bypass routing, use direct interface | |
* These flags are _unsupported_ as of ns-3.1. | |
* | |
* \param p ns3::Packet to send | |
* \param flags Socket control flags | |
* \returns the number of bytes accepted for transmission if no error | |
* occurs, and -1 otherwise. | |
* | |
* \see SetSendCallback | |
*/ | |
virtual int Send (Ptr<Packet> p, uint32_t flags) = 0; |
虚函数,需要查看子类的实现
因为本人最常用的是 UdpSocket ,所以拿 UdpSocket 为例。
UdpSocket 里不包含 Send 函数,所以其实现是在子类 UdpSocketImpl 里面
int | |
UdpSocketImpl::Send (Ptr<Packet> p, uint32_t flags) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << p << flags); | |
if (!m_connected) | |
{ | |
m_errno = ERROR_NOTCONN; | |
return -1; | |
} | |
return DoSend (p); | |
} | |
int | |
UdpSocketImpl::DoSend (Ptr<Packet> p) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << p); | |
if ((m_endPoint == 0) && (Ipv4Address::IsMatchingType(m_defaultAddress) == true)) | |
{ | |
if (Bind () == -1) | |
{ | |
NS_ASSERT (m_endPoint == 0); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
NS_ASSERT (m_endPoint != 0); | |
} | |
else if ((m_endPoint6 == 0) && (Ipv6Address::IsMatchingType(m_defaultAddress) == true)) | |
{ | |
if (Bind6 () == -1) | |
{ | |
NS_ASSERT (m_endPoint6 == 0); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
NS_ASSERT (m_endPoint6 != 0); | |
} | |
if (m_shutdownSend) | |
{ | |
m_errno = ERROR_SHUTDOWN; | |
return -1; | |
} | |
if (Ipv4Address::IsMatchingType (m_defaultAddress)) | |
{ | |
return DoSendTo (p, Ipv4Address::ConvertFrom (m_defaultAddress), m_defaultPort, GetIpTos ()); | |
} | |
else if (Ipv6Address::IsMatchingType (m_defaultAddress)) | |
{ | |
return DoSendTo (p, Ipv6Address::ConvertFrom (m_defaultAddress), m_defaultPort); | |
} | |
m_errno = ERROR_AFNOSUPPORT; | |
return(-1); | |
} |
Send 方法调用 DoSend 方法,其中 DoSend 方法做了一些判断,判断 socket 实现已经 bind 和 connection 。
UdpSocketImpl::DoSend 方法又调用了 DoSendTo 方法,分为两种情况,一种是 IPV4 ,一种是 IPV6 .
这里还是以 Ipv4 为例说明。
int | |
UdpSocketImpl::DoSendTo (Ptr<Packet> p, Ipv4Address dest, uint16_t port, uint8_t tos) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << p << dest << port << (uint16_t) tos); | |
if (m_boundnetdevice) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Bound interface number " << m_boundnetdevice->GetIfIndex ()); | |
} | |
if (m_endPoint == 0) | |
{ | |
if (Bind () == -1) | |
{ | |
NS_ASSERT (m_endPoint == 0); | |
return -1; | |
} | |
NS_ASSERT (m_endPoint != 0); | |
} | |
if (m_shutdownSend) | |
{ | |
m_errno = ERROR_SHUTDOWN; | |
return -1; | |
} | |
if (p->GetSize () > GetTxAvailable () ) | |
{ | |
m_errno = ERROR_MSGSIZE; | |
return -1; | |
} | |
uint8_t priority = GetPriority (); | |
if (tos) | |
{ | |
SocketIpTosTag ipTosTag; | |
ipTosTag.SetTos (tos); | |
// This packet may already have a SocketIpTosTag (see BUG 2440) | |
p->ReplacePacketTag (ipTosTag); | |
priority = IpTos2Priority (tos); | |
} | |
if (priority) | |
{ | |
SocketPriorityTag priorityTag; | |
priorityTag.SetPriority (priority); | |
p->ReplacePacketTag (priorityTag); | |
} | |
Ptr<Ipv4> ipv4 = m_node->GetObject<Ipv4> (); | |
// Locally override the IP TTL for this socket | |
// We cannot directly modify the TTL at this stage, so we set a Packet tag | |
// The destination can be either multicast, unicast/anycast, or | |
// either all-hosts broadcast or limited (subnet-directed) broadcast. | |
// For the latter two broadcast types, the TTL will later be set to one | |
// irrespective of what is set in these socket options. So, this tagging | |
// may end up setting the TTL of a limited broadcast packet to be | |
// the same as a unicast, but it will be fixed further down the stack | |
if (m_ipMulticastTtl != 0 && dest.IsMulticast ()) | |
{ | |
SocketIpTtlTag tag; | |
tag.SetTtl (m_ipMulticastTtl); | |
p->AddPacketTag (tag); | |
} | |
else if (IsManualIpTtl () && GetIpTtl () != 0 && !dest.IsMulticast () && !dest.IsBroadcast ()) | |
{ | |
SocketIpTtlTag tag; | |
tag.SetTtl (GetIpTtl ()); | |
p->AddPacketTag (tag); | |
} | |
{ | |
SocketSetDontFragmentTag tag; | |
bool found = p->RemovePacketTag (tag); | |
if (!found) | |
{ | |
if (m_mtuDiscover) | |
{ | |
tag.Enable (); | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
tag.Disable (); | |
} | |
p->AddPacketTag (tag); | |
} | |
} | |
// Note that some systems will only send limited broadcast packets | |
// out of the "default" interface; here we send it out all interfaces | |
if (dest.IsBroadcast ()) | |
{ | |
if (!m_allowBroadcast) | |
{ | |
m_errno = ERROR_OPNOTSUPP; | |
return -1; | |
} | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Limited broadcast start."); | |
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < ipv4->GetNInterfaces (); i++ ) | |
{ | |
// Get the primary address | |
Ipv4InterfaceAddress iaddr = ipv4->GetAddress (i, 0); | |
Ipv4Address addri = iaddr.GetLocal (); | |
if (addri == Ipv4Address ("127.0.0.1")) | |
continue; | |
// Check if interface-bound socket | |
if (m_boundnetdevice) | |
{ | |
if (ipv4->GetNetDevice (i) != m_boundnetdevice) | |
continue; | |
} | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Sending one copy from " << addri << " to " << dest); | |
m_udp->Send (p->Copy (), addri, dest, | |
m_endPoint->GetLocalPort (), port); | |
NotifyDataSent (p->GetSize ()); | |
NotifySend (GetTxAvailable ()); | |
} | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Limited broadcast end."); | |
return p->GetSize (); | |
} | |
else if (m_endPoint->GetLocalAddress () != Ipv4Address::GetAny ()) | |
{ | |
m_udp->Send (p->Copy (), m_endPoint->GetLocalAddress (), dest, | |
m_endPoint->GetLocalPort (), port, 0); | |
NotifyDataSent (p->GetSize ()); | |
NotifySend (GetTxAvailable ()); | |
return p->GetSize (); | |
} | |
else if (ipv4->GetRoutingProtocol () != 0) | |
{ | |
Ipv4Header header; | |
header.SetDestination (dest); | |
header.SetProtocol (UdpL4Protocol::PROT_NUMBER); | |
Socket::SocketErrno errno_; | |
Ptr<Ipv4Route> route; | |
Ptr<NetDevice> oif = m_boundnetdevice; //specify non-zero if bound to a specific device | |
// TBD-- we could cache the route and just check its validity | |
route = ipv4->GetRoutingProtocol ()->RouteOutput (p, header, oif, errno_); | |
if (route != 0) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Route exists"); | |
if (!m_allowBroadcast) | |
{ | |
// Here we try to route subnet-directed broadcasts | |
uint32_t outputIfIndex = ipv4->GetInterfaceForDevice (route->GetOutputDevice ()); | |
uint32_t ifNAddr = ipv4->GetNAddresses (outputIfIndex); | |
for (uint32_t addrI = 0; addrI < ifNAddr; ++addrI) | |
{ | |
Ipv4InterfaceAddress ifAddr = ipv4->GetAddress (outputIfIndex, addrI); | |
if (dest == ifAddr.GetBroadcast ()) | |
{ | |
m_errno = ERROR_OPNOTSUPP; | |
return -1; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
header.SetSource (route->GetSource ()); | |
m_udp->Send (p->Copy (), header.GetSource (), header.GetDestination (), | |
m_endPoint->GetLocalPort (), port, route); | |
NotifyDataSent (p->GetSize ()); | |
return p->GetSize (); | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("No route to destination"); | |
NS_LOG_ERROR (errno_); | |
m_errno = errno_; | |
return -1; | |
} | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_ERROR ("ERROR_NOROUTETOHOST"); | |
m_errno = ERROR_NOROUTETOHOST; | |
return -1; | |
} | |
return 0; | |
} |
这里面有一个关键的步骤就是 Socket 发送的时候只知道目的节点 dest ,在传输的过程中,我们需要知道下一跳的节点 next 是什么?通常来说这是由配置的路由协议来决定的,这节的重点不是路由,所以我们先跳过这点,只需知道,在这时,已经找到了下一跳 next 。
// TBD-- we could cache the route and just check its validity | |
route = ipv4->GetRoutingProtocol ()->RouteOutput (p, header, oif, errno_); |
回到函数中,我们可以看到得到 next 后,下一步调用的是 m_udp->Send
m_udp->Send (p->Copy (), header.GetSource (), header.GetDestination (), | |
m_endPoint->GetLocalPort (), port, route); |
其中的 m_udp 对象就是 UdpL4Protocol 类对象,所以下一步是调用的 UdpL4Protocol::Send
void | |
UdpL4Protocol::Send (Ptr<Packet> packet, | |
Ipv4Address saddr, Ipv4Address daddr, | |
uint16_t sport, uint16_t dport) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << packet << saddr << daddr << sport << dport); | |
UdpHeader udpHeader; | |
if(Node::ChecksumEnabled ()) | |
{ | |
udpHeader.EnableChecksums (); | |
udpHeader.InitializeChecksum (saddr, | |
daddr, | |
PROT_NUMBER); | |
} | |
udpHeader.SetDestinationPort (dport); | |
udpHeader.SetSourcePort (sport); | |
packet->AddHeader (udpHeader); | |
m_downTarget (packet, saddr, daddr, PROT_NUMBER, 0); | |
} |
这里 UdpL4Protocol::Send 方法调用了一个 m_downTarget 的回调地址。 m_downTarget 的值的设置代码如下:
/* | |
* This method is called by AggregateObject and completes the aggregation | |
* by setting the node in the udp stack and link it to the ipv4 object | |
* present in the node along with the socket factory | |
*/ | |
void | |
UdpL4Protocol::NotifyNewAggregate () | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this); | |
Ptr<Node> node = this->GetObject<Node> (); | |
Ptr<Ipv4> ipv4 = this->GetObject<Ipv4> (); | |
Ptr<Ipv6> ipv6 = node->GetObject<Ipv6> (); | |
if (m_node == 0) | |
{ | |
if ((node != 0) && (ipv4 != 0 || ipv6 != 0)) | |
{ | |
this->SetNode (node); | |
Ptr<UdpSocketFactoryImpl> udpFactory = CreateObject<UdpSocketFactoryImpl> (); | |
udpFactory->SetUdp (this); | |
node->AggregateObject (udpFactory); | |
} | |
} | |
// We set at least one of our 2 down targets to the IPv4/IPv6 send | |
// functions. Since these functions have different prototypes, we | |
// need to keep track of whether we are connected to an IPv4 or | |
// IPv6 lower layer and call the appropriate one. | |
if (ipv4 != 0 && m_downTarget.IsNull()) | |
{ | |
ipv4->Insert (this); | |
this->SetDownTarget (MakeCallback (&Ipv4::Send, ipv4)); | |
} | |
if (ipv6 != 0 && m_downTarget6.IsNull()) | |
{ | |
ipv6->Insert (this); | |
this->SetDownTarget6 (MakeCallback (&Ipv6::Send, ipv6)); | |
} | |
IpL4Protocol::NotifyNewAggregate (); | |
} |
所以实际调用的是 Ipv4::Send
virtual void Send (Ptr<Packet> packet, Ipv4Address source, | |
Ipv4Address destination, uint8_t protocol, Ptr<Ipv4Route> route) = 0; |
是个虚函数,所以同样看其子类
这里我们也同样只看其中一个, Ipv4L3Protocol
void | |
Ipv4L3Protocol::Send (Ptr<Packet> packet, | |
Ipv4Address source, | |
Ipv4Address destination, | |
uint8_t protocol, | |
Ptr<Ipv4Route> route) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << packet << source << destination << uint32_t (protocol) << route); | |
bool mayFragment = true; | |
// we need a copy of the packet with its tags in case we need to invoke recursion. | |
Ptr<Packet> pktCopyWithTags = packet->Copy (); | |
uint8_t ttl = m_defaultTtl; | |
SocketIpTtlTag ipTtlTag; | |
bool ipTtlTagFound = packet->RemovePacketTag (ipTtlTag); | |
if (ipTtlTagFound) | |
{ | |
ttl = ipTtlTag.GetTtl (); | |
} | |
uint8_t tos = 0; | |
SocketIpTosTag ipTosTag; | |
bool ipTosTagFound = packet->RemovePacketTag (ipTosTag); | |
if (ipTosTagFound) | |
{ | |
tos = ipTosTag.GetTos (); | |
} | |
// can construct the header here | |
Ipv4Header ipHeader = BuildHeader (source, destination, protocol, packet->GetSize (), ttl, tos, mayFragment); | |
// Handle a few cases: | |
// 1) packet is passed in with a route entry | |
// 1a) packet is passed in with a route entry but route->GetGateway is not set (e.g., on-demand) | |
// 1b) packet is passed in with a route entry and valid gateway | |
// 2) packet is passed without a route and packet is destined to limited broadcast address | |
// 3) packet is passed without a route and packet is destined to a subnet-directed broadcast address | |
// 4) packet is passed without a route, packet is not broadcast (e.g., a raw socket call, or ICMP) | |
// 1) packet is passed in with route entry | |
if (route) | |
{ | |
// 1a) route->GetGateway is not set (e.g., on-demand) | |
if (!route->GetGateway ().IsInitialized ()) | |
{ | |
// This could arise because the synchronous RouteOutput() call | |
// returned to the transport protocol with a source address but | |
// there was no next hop available yet (since a route may need | |
// to be queried). | |
NS_FATAL_ERROR ("Ipv4L3Protocol::Send case 1a: packet passed with a route but the Gateway address is uninitialized. This case not yet implemented."); | |
} | |
// 1b) with a valid gateway | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Ipv4L3Protocol::Send case 1b: passed in with route and valid gateway"); | |
int32_t interface = GetInterfaceForDevice (route->GetOutputDevice ()); | |
m_sendOutgoingTrace (ipHeader, packet, interface); | |
SendRealOut (route, packet->Copy (), ipHeader); | |
return; | |
} | |
// 2) packet is destined to limited broadcast address or link-local multicast address | |
if (destination.IsBroadcast () || destination.IsLocalMulticast ()) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Ipv4L3Protocol::Send case 2: limited broadcast - no route"); | |
uint32_t ifaceIndex = 0; | |
for (Ipv4InterfaceList::iterator ifaceIter = m_interfaces.begin (); | |
ifaceIter != m_interfaces.end (); ifaceIter++, ifaceIndex++) | |
{ | |
Ptr<Ipv4Interface> outInterface = *ifaceIter; | |
// ANY source matches any interface | |
bool sendIt = source.IsAny (); | |
// check if some specific address on outInterface matches | |
for (uint32_t index = 0; !sendIt && index < outInterface->GetNAddresses (); index++) | |
{ | |
if (outInterface->GetAddress (index).GetLocal () == source) | |
{ | |
sendIt = true; | |
} | |
} | |
if (sendIt) | |
{ | |
// create a proxy route for this interface | |
Ptr<Ipv4Route> route = Create<Ipv4Route> (); | |
route->SetDestination (destination); | |
route->SetGateway (Ipv4Address::GetAny ()); | |
route->SetSource (source); | |
route->SetOutputDevice (outInterface->GetDevice ()); | |
DecreaseIdentification (source, destination, protocol); | |
Send (pktCopyWithTags, source, destination, protocol, route); | |
} | |
} | |
return; | |
} | |
// 3) check: packet is destined to a subnet-directed broadcast address | |
for (Ipv4InterfaceList::iterator ifaceIter = m_interfaces.begin (); | |
ifaceIter != m_interfaces.end (); ifaceIter++) | |
{ | |
Ptr<Ipv4Interface> outInterface = *ifaceIter; | |
uint32_t ifaceIndex = GetInterfaceForDevice (outInterface->GetDevice ()); | |
for (uint32_t j = 0; j < GetNAddresses (ifaceIndex); j++) | |
{ | |
Ipv4InterfaceAddress ifAddr = GetAddress (ifaceIndex, j); | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Testing address " << ifAddr.GetLocal () << " with mask " << ifAddr.GetMask ()); | |
if (destination.IsSubnetDirectedBroadcast (ifAddr.GetMask ()) && | |
destination.CombineMask (ifAddr.GetMask ()) == ifAddr.GetLocal ().CombineMask (ifAddr.GetMask ()) ) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Ipv4L3Protocol::Send case 3: subnet directed bcast to " << ifAddr.GetLocal () << " - no route"); | |
// create a proxy route for this interface | |
Ptr<Ipv4Route> route = Create<Ipv4Route> (); | |
route->SetDestination (destination); | |
route->SetGateway (Ipv4Address::GetAny ()); | |
route->SetSource (source); | |
route->SetOutputDevice (outInterface->GetDevice ()); | |
DecreaseIdentification (source, destination, protocol); | |
Send (pktCopyWithTags, source, destination, protocol, route); | |
return; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
// 4) packet is not broadcast, and route is NULL (e.g., a raw socket call) | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Ipv4L3Protocol::Send case 4: not broadcast and passed in with no route " << destination); | |
Socket::SocketErrno errno_; | |
Ptr<NetDevice> oif (0); // unused for now | |
Ptr<Ipv4Route> newRoute; | |
if (m_routingProtocol != 0) | |
{ | |
newRoute = m_routingProtocol->RouteOutput (packet, ipHeader, oif, errno_); | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_ERROR ("Ipv4L3Protocol::Send: m_routingProtocol == 0"); | |
} | |
if (newRoute) | |
{ | |
DecreaseIdentification (source, destination, protocol); | |
Send (pktCopyWithTags, source, destination, protocol, newRoute); | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_WARN ("No route to host. Drop."); | |
m_dropTrace (ipHeader, packet, DROP_NO_ROUTE, m_node->GetObject<Ipv4> (), 0); | |
DecreaseIdentification (source, destination, protocol); | |
} | |
} |
这个函数里对是否有 route 做了五种情况的区分。最终都会走到 Ipv4L3Protocol::SendRealOut
void | |
Ipv4L3Protocol::SendRealOut (Ptr<Ipv4Route> route, | |
Ptr<Packet> packet, | |
Ipv4Header const &ipHeader) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << route << packet << &ipHeader); | |
if (route == 0) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_WARN ("No route to host. Drop."); | |
m_dropTrace (ipHeader, packet, DROP_NO_ROUTE, m_node->GetObject<Ipv4> (), 0); | |
return; | |
} | |
Ptr<NetDevice> outDev = route->GetOutputDevice (); | |
int32_t interface = GetInterfaceForDevice (outDev); | |
NS_ASSERT (interface >= 0); | |
Ptr<Ipv4Interface> outInterface = GetInterface (interface); | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Send via NetDevice ifIndex " << outDev->GetIfIndex () << " ipv4InterfaceIndex " << interface); | |
Ipv4Address target; | |
std::string targetLabel; | |
if (route->GetGateway ().IsAny ()) | |
{ | |
target = ipHeader.GetDestination (); | |
targetLabel = "destination"; | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
target = route->GetGateway (); | |
targetLabel = "gateway"; | |
} | |
if (outInterface->IsUp ()) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Send to " << targetLabel << " " << target); | |
if ( packet->GetSize () + ipHeader.GetSerializedSize () > outInterface->GetDevice ()->GetMtu () ) | |
{ | |
std::list<Ipv4PayloadHeaderPair> listFragments; | |
DoFragmentation (packet, ipHeader, outInterface->GetDevice ()->GetMtu (), listFragments); | |
for ( std::list<Ipv4PayloadHeaderPair>::iterator it = listFragments.begin (); it != listFragments.end (); it++ ) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Sending fragment " << *(it->first) ); | |
CallTxTrace (it->second, it->first, m_node->GetObject<Ipv4> (), interface); | |
outInterface->Send (it->first, it->second, target); | |
} | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
CallTxTrace (ipHeader, packet, m_node->GetObject<Ipv4> (), interface); | |
outInterface->Send (packet, ipHeader, target); | |
} | |
} | |
} |
outInterface 的类型是 Ipv4Interface ,所以下一步就是
void | |
Ipv4Interface::Send (Ptr<Packet> p, const Ipv4Header & hdr, Ipv4Address dest) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << *p << dest); | |
if (!IsUp ()) | |
{ | |
return; | |
} | |
// Check for a loopback device, if it's the case we don't pass through | |
// traffic control layer | |
if (DynamicCast<LoopbackNetDevice> (m_device)) | |
{ | |
/// \todo additional checks needed here (such as whether multicast | |
/// goes to loopback)? | |
p->AddHeader (hdr); | |
m_device->Send (p, m_device->GetBroadcast (), Ipv4L3Protocol::PROT_NUMBER); | |
return; | |
} | |
NS_ASSERT (m_tc != 0); | |
// is this packet aimed at a local interface ? | |
for (Ipv4InterfaceAddressListCI i = m_ifaddrs.begin (); i != m_ifaddrs.end (); ++i) | |
{ | |
if (dest == (*i).GetLocal ()) | |
{ | |
p->AddHeader (hdr); | |
m_tc->Receive (m_device, p, Ipv4L3Protocol::PROT_NUMBER, | |
m_device->GetBroadcast (), | |
m_device->GetBroadcast (), | |
NetDevice::PACKET_HOST); | |
return; | |
} | |
} | |
if (m_device->NeedsArp ()) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Needs ARP" << " " << dest); | |
Ptr<ArpL3Protocol> arp = m_node->GetObject<ArpL3Protocol> (); | |
Address hardwareDestination; | |
bool found = false; | |
if (dest.IsBroadcast ()) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("All-network Broadcast"); | |
hardwareDestination = m_device->GetBroadcast (); | |
found = true; | |
} | |
else if (dest.IsMulticast ()) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("IsMulticast"); | |
NS_ASSERT_MSG (m_device->IsMulticast (), | |
"ArpIpv4Interface::SendTo (): Sending multicast packet over " | |
"non-multicast device"); | |
hardwareDestination = m_device->GetMulticast (dest); | |
found = true; | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
for (Ipv4InterfaceAddressListCI i = m_ifaddrs.begin (); i != m_ifaddrs.end (); ++i) | |
{ | |
if (dest.IsSubnetDirectedBroadcast ((*i).GetMask ())) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Subnetwork Broadcast"); | |
hardwareDestination = m_device->GetBroadcast (); | |
found = true; | |
break; | |
} | |
} | |
if (!found) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("ARP Lookup"); | |
found = arp->Lookup (p, hdr, dest, m_device, m_cache, &hardwareDestination); | |
} | |
} | |
if (found) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Address Resolved. Send."); | |
m_tc->Send (m_device, Create<Ipv4QueueDiscItem> (p, hardwareDestination, Ipv4L3Protocol::PROT_NUMBER, hdr)); | |
} | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Doesn't need ARP"); | |
m_tc->Send (m_device, Create<Ipv4QueueDiscItem> (p, m_device->GetBroadcast (), Ipv4L3Protocol::PROT_NUMBER, hdr)); | |
} | |
} |
m_tc 类型是 Ipv4Interface 的 Send 方法会做一些判断,广播,多播、子网广播、ARP 等,处理不同。 m_tc 对象就是 TrafficControlLayer 类对象。
void | |
TrafficControlLayer::Send (Ptr<NetDevice> device, Ptr<QueueDiscItem> item) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << device << item); | |
NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Send packet to device " << device << " protocol number " << | |
item->GetProtocol ()); | |
Ptr<NetDeviceQueueInterface> devQueueIface; | |
std::map<Ptr<NetDevice>, NetDeviceInfo>::iterator ndi = m_netDevices.find (device); | |
if (ndi != m_netDevices.end ()) | |
{ | |
devQueueIface = ndi->second.m_ndqi; | |
} | |
// determine the transmission queue of the device where the packet will be enqueued | |
std::size_t txq = 0; | |
if (devQueueIface && devQueueIface->GetNTxQueues () > 1) | |
{ | |
txq = devQueueIface->GetSelectQueueCallback () (item); | |
// otherwise, Linux determines the queue index by using a hash function | |
// and associates such index to the socket which the packet belongs to, | |
// so that subsequent packets of the same socket will be mapped to the | |
// same tx queue (__netdev_pick_tx function in net/core/dev.c). It is | |
// pointless to implement this in ns-3 because currently the multi-queue | |
// devices provide a select queue callback | |
} | |
NS_ASSERT (!devQueueIface || txq < devQueueIface->GetNTxQueues ()); | |
if (ndi == m_netDevices.end () || ndi->second.m_rootQueueDisc == 0) | |
{ | |
// The device has no attached queue disc, thus add the header to the packet and | |
// send it directly to the device if the selected queue is not stopped | |
if (!devQueueIface || !devQueueIface->GetTxQueue (txq)->IsStopped ()) | |
{ | |
item->AddHeader (); | |
// a single queue device makes no use of the priority tag | |
if (!devQueueIface || devQueueIface->GetNTxQueues () == 1) | |
{ | |
SocketPriorityTag priorityTag; | |
item->GetPacket ()->RemovePacketTag (priorityTag); | |
} | |
device->Send (item->GetPacket (), item->GetAddress (), item->GetProtocol ()); | |
} | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
// Enqueue the packet in the queue disc associated with the netdevice queue | |
// selected for the packet and try to dequeue packets from such queue disc | |
item->SetTxQueueIndex (txq); | |
Ptr<QueueDisc> qDisc = ndi->second.m_queueDiscsToWake[txq]; | |
NS_ASSERT (qDisc); | |
qDisc->Enqueue (item); | |
qDisc->Run (); | |
} | |
} |
TrafficControlLayer::Send 方法会通过 device->Send 发送 packet 。
其中的 device 对象就是 WiFiNetDevice 对象。
由此,完成了 packet 从 socket 对象到 netdevice 的发送过程。之后就是上一节的内容了
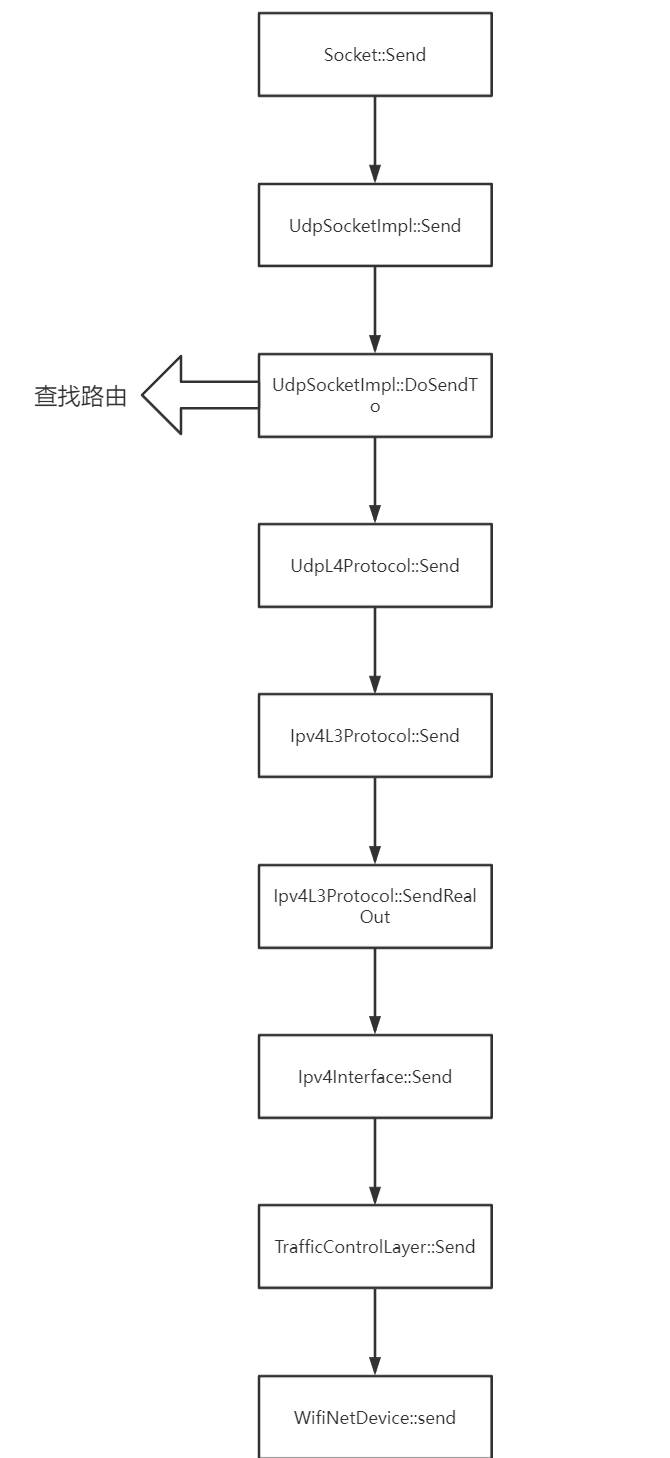
# 发送过程流程图
# 接收过程分析
首先回到上节描述的 WifiNetDevice::ForwardUp :
void | |
WifiNetDevice::ForwardUp (Ptr<const Packet> packet, Mac48Address from, Mac48Address to) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << packet << from << to); | |
LlcSnapHeader llc; | |
NetDevice::PacketType type; | |
if (to.IsBroadcast ()) | |
{ | |
type = NetDevice::PACKET_BROADCAST; | |
} | |
else if (to.IsGroup ()) | |
{ | |
type = NetDevice::PACKET_MULTICAST; | |
} | |
else if (to == m_mac->GetAddress ()) | |
{ | |
type = NetDevice::PACKET_HOST; | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
type = NetDevice::PACKET_OTHERHOST; | |
} | |
Ptr<Packet> copy = packet->Copy (); | |
if (type != NetDevice::PACKET_OTHERHOST) | |
{ | |
m_mac->NotifyRx (packet); | |
copy->RemoveHeader (llc); | |
m_forwardUp (this, copy, llc.GetType (), from); | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
copy->RemoveHeader (llc); | |
} | |
if (!m_promiscRx.IsNull ()) | |
{ | |
m_mac->NotifyPromiscRx (copy); | |
m_promiscRx (this, copy, llc.GetType (), from, to, type); | |
} | |
} |
这里主要是两个回调,一个是 m_forwardUp ,另一个是 m_promiscRx 。
m_forwardUp 的设置是在 Node.cc
uint32_t | |
Node::AddDevice (Ptr<NetDevice> device) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << device); | |
uint32_t index = m_devices.size (); | |
m_devices.push_back (device); | |
device->SetNode (this); | |
device->SetIfIndex (index); | |
device->SetReceiveCallback (MakeCallback (&Node::NonPromiscReceiveFromDevice, this)); | |
Simulator::ScheduleWithContext (GetId (), Seconds (0.0), | |
&NetDevice::Initialize, device); | |
NotifyDeviceAdded (device); | |
return index; | |
} |
所以实际调用的是 Node::NonPromiscReceiveFromDevice
bool | |
Node::NonPromiscReceiveFromDevice (Ptr<NetDevice> device, Ptr<const Packet> packet, uint16_t protocol, | |
const Address &from) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << device << packet << protocol << &from); | |
return ReceiveFromDevice (device, packet, protocol, from, device->GetAddress (), NetDevice::PacketType (0), false); | |
} | |
bool | |
Node::ReceiveFromDevice (Ptr<NetDevice> device, Ptr<const Packet> packet, uint16_t protocol, | |
const Address &from, const Address &to, NetDevice::PacketType packetType, bool promiscuous) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << device << packet << protocol << &from << &to << packetType << promiscuous); | |
NS_ASSERT_MSG (Simulator::GetContext () == GetId (), "Received packet with erroneous context ; " << | |
"make sure the channels in use are correctly updating events context " << | |
"when transferring events from one node to another."); | |
NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Node " << GetId () << " ReceiveFromDevice: dev " | |
<< device->GetIfIndex () << " (type=" << device->GetInstanceTypeId ().GetName () | |
<< ") Packet UID " << packet->GetUid ()); | |
bool found = false; | |
for (ProtocolHandlerList::iterator i = m_handlers.begin (); | |
i != m_handlers.end (); i++) | |
{ | |
if (i->device == 0 || | |
(i->device != 0 && i->device == device)) | |
{ | |
if (i->protocol == 0 || | |
i->protocol == protocol) | |
{ | |
if (promiscuous == i->promiscuous) | |
{ | |
i->handler (device, packet, protocol, from, to, packetType); | |
found = true; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
return found; | |
} |
Node::NonPromiscReceiveFromDevice 方法调用 Node::ReceiveFromDevice 方法,方法内部会循环判断是否是合适的处理 packet 的协议,如果有, found 为 true ,则就有由协议来处理 packet 。
m_handlers 的值是通过 Node::RegisterProtocolHandler 方法设置的。代码如下:
void | |
Node::RegisterProtocolHandler (ProtocolHandler handler, | |
uint16_t protocolType, | |
Ptr<NetDevice> device, | |
bool promiscuous) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << &handler << protocolType << device << promiscuous); | |
struct Node::ProtocolHandlerEntry entry; | |
entry.handler = handler; | |
entry.protocol = protocolType; | |
entry.device = device; | |
entry.promiscuous = promiscuous; | |
// On demand enable promiscuous mode in netdevices | |
if (promiscuous) | |
{ | |
if (device == 0) | |
{ | |
for (std::vector<Ptr<NetDevice> >::iterator i = m_devices.begin (); | |
i != m_devices.end (); i++) | |
{ | |
Ptr<NetDevice> dev = *i; | |
dev->SetPromiscReceiveCallback (MakeCallback (&Node::PromiscReceiveFromDevice, this)); | |
} | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
device->SetPromiscReceiveCallback (MakeCallback (&Node::PromiscReceiveFromDevice, this)); | |
} | |
} | |
m_handlers.push_back (entry); | |
} |
通过全局搜索的话,调用 Node::RegisterProtocolHandler 方法的地方有很多,但总的来说都是根据配置的协议来选择的,这里我们以 TrafficControlLayer::Receive 为例。
void | |
TrafficControlLayer::Receive (Ptr<NetDevice> device, Ptr<const Packet> p, | |
uint16_t protocol, const Address &from, const Address &to, | |
NetDevice::PacketType packetType) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << device << p << protocol << from << to << packetType); | |
bool found = false; | |
for (ProtocolHandlerList::iterator i = m_handlers.begin (); | |
i != m_handlers.end (); i++) | |
{ | |
if (i->device == 0 | |
|| (i->device != 0 && i->device == device)) | |
{ | |
if (i->protocol == 0 | |
|| i->protocol == protocol) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Found handler for packet " << p << ", protocol " << | |
protocol << " and NetDevice " << device << | |
". Send packet up"); | |
i->handler (device, p, protocol, from, to, packetType); | |
found = true; | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
NS_ABORT_MSG_IF (!found, "Handler for protocol " << p << " and device " << device << | |
" not found. It isn't forwarded up; it dies here."); | |
} |
在这里也涉及到一个 m_handlers
其设置方式为 TrafficControlLayer::RegisterProtocolHandler
TrafficControlLayer::RegisterProtocolHandler (Node::ProtocolHandler handler, | |
uint16_t protocolType, Ptr<NetDevice> device) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << protocolType << device); | |
struct ProtocolHandlerEntry entry; | |
entry.handler = handler; | |
entry.protocol = protocolType; | |
entry.device = device; | |
entry.promiscuous = false; | |
m_handlers.push_back (entry); | |
NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Handler for NetDevice: " << device << " registered for protocol " << | |
protocolType << "."); | |
} |
同样的,我们全局搜索该调用方式
可以看出主要是这两种调用方式
tc->RegisterProtocolHandler (MakeCallback (&Ipv4L3Protocol::Receive, this), | |
Ipv4L3Protocol::PROT_NUMBER, device); | |
tc->RegisterProtocolHandler (MakeCallback (&ArpL3Protocol::Receive, PeekPointer (GetObject<ArpL3Protocol> ())), | |
ArpL3Protocol::PROT_NUMBER, device); |
具体执行哪里,要看使用的协议。对于 packet 数据包来说,处理起来就是 Ipv4L3Protocol::Receive ,如果使用到了 ARP 协议,处理起来就是 ArpL3Protocol::Receive 。
这里以 Ipv4L3Protocol::Receive 为例说明。
void | |
Ipv4L3Protocol::Receive ( Ptr<NetDevice> device, Ptr<const Packet> p, uint16_t protocol, const Address &from, | |
const Address &to, NetDevice::PacketType packetType) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << device << p << protocol << from << to << packetType); | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Packet from " << from << " received on node " << | |
m_node->GetId ()); | |
int32_t interface = GetInterfaceForDevice(device); | |
NS_ASSERT_MSG (interface != -1, "Received a packet from an interface that is not known to IPv4"); | |
Ptr<Packet> packet = p->Copy (); | |
Ptr<Ipv4Interface> ipv4Interface = m_interfaces[interface]; | |
if (ipv4Interface->IsUp ()) | |
{ | |
m_rxTrace (packet, m_node->GetObject<Ipv4> (), interface); | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Dropping received packet -- interface is down"); | |
Ipv4Header ipHeader; | |
packet->RemoveHeader (ipHeader); | |
m_dropTrace (ipHeader, packet, DROP_INTERFACE_DOWN, m_node->GetObject<Ipv4> (), interface); | |
return; | |
} | |
Ipv4Header ipHeader; | |
if (Node::ChecksumEnabled ()) | |
{ | |
ipHeader.EnableChecksum (); | |
} | |
packet->RemoveHeader (ipHeader); | |
// Trim any residual frame padding from underlying devices | |
if (ipHeader.GetPayloadSize () < packet->GetSize ()) | |
{ | |
packet->RemoveAtEnd (packet->GetSize () - ipHeader.GetPayloadSize ()); | |
} | |
if (!ipHeader.IsChecksumOk ()) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Dropping received packet -- checksum not ok"); | |
m_dropTrace (ipHeader, packet, DROP_BAD_CHECKSUM, m_node->GetObject<Ipv4> (), interface); | |
return; | |
} | |
// the packet is valid, we update the ARP cache entry (if present) | |
Ptr<ArpCache> arpCache = ipv4Interface->GetArpCache (); | |
if (arpCache) | |
{ | |
// case one, it's a a direct routing. | |
ArpCache::Entry *entry = arpCache->Lookup (ipHeader.GetSource ()); | |
if (entry) | |
{ | |
if (entry->IsAlive ()) | |
{ | |
entry->UpdateSeen (); | |
} | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
// It's not in the direct routing, so it's the router, and it could have multiple IP addresses. | |
// In doubt, update all of them. | |
// Note: it's a confirmed behavior for Linux routers. | |
std::list<ArpCache::Entry *> entryList = arpCache->LookupInverse (from); | |
std::list<ArpCache::Entry *>::iterator iter; | |
for (iter = entryList.begin (); iter != entryList.end (); iter ++) | |
{ | |
if ((*iter)->IsAlive ()) | |
{ | |
(*iter)->UpdateSeen (); | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
for (SocketList::iterator i = m_sockets.begin (); i != m_sockets.end (); ++i) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Forwarding to raw socket"); | |
Ptr<Ipv4RawSocketImpl> socket = *i; | |
socket->ForwardUp (packet, ipHeader, ipv4Interface); | |
} | |
if (m_enableDpd && ipHeader.GetDestination ().IsMulticast () && UpdateDuplicate (packet, ipHeader)) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Dropping received packet -- duplicate."); | |
m_dropTrace (ipHeader, packet, DROP_DUPLICATE, m_node->GetObject<Ipv4> (), interface); | |
return; | |
} | |
NS_ASSERT_MSG (m_routingProtocol != 0, "Need a routing protocol object to process packets"); | |
if (!m_routingProtocol->RouteInput (packet, ipHeader, device, | |
MakeCallback (&Ipv4L3Protocol::IpForward, this), | |
MakeCallback (&Ipv4L3Protocol::IpMulticastForward, this), | |
MakeCallback (&Ipv4L3Protocol::LocalDeliver, this), | |
MakeCallback (&Ipv4L3Protocol::RouteInputError, this) | |
)) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_WARN ("No route found for forwarding packet. Drop."); | |
m_dropTrace (ipHeader, packet, DROP_NO_ROUTE, m_node->GetObject<Ipv4> (), interface); | |
} | |
} |
在该函数中主要分两部分,如果 m_sockets 不为空的话,直接 socket::ForwardUp ,否则通过 m_routingProtocol->RouteInput 交付。 m_routingProtocol 类型是 Ipv4RoutingProtocol ,我们按照 Ipv4RoutingProtocol::RouteInput 进行探索。
virtual bool RouteInput (Ptr<const Packet> p, const Ipv4Header &header, Ptr<const NetDevice> idev, | |
UnicastForwardCallback ucb, MulticastForwardCallback mcb, | |
LocalDeliverCallback lcb, ErrorCallback ecb) = 0; |
其实现方式是由子类来决定。这涉及到路由协议的部分,会在今后的章节进行介绍。
但都会调用 LocalDeliverCallback lcb ,即 LocalDeliver 方法
void | |
Ipv4L3Protocol::LocalDeliver (Ptr<const Packet> packet, Ipv4Header const&ip, uint32_t iif) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << packet << &ip << iif); | |
Ptr<Packet> p = packet->Copy (); // need to pass a non-const packet up | |
Ipv4Header ipHeader = ip; | |
if ( !ipHeader.IsLastFragment () || ipHeader.GetFragmentOffset () != 0 ) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Received a fragment, processing " << *p ); | |
bool isPacketComplete; | |
isPacketComplete = ProcessFragment (p, ipHeader, iif); | |
if ( isPacketComplete == false) | |
{ | |
return; | |
} | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("Got last fragment, Packet is complete " << *p ); | |
ipHeader.SetFragmentOffset (0); | |
ipHeader.SetPayloadSize (p->GetSize ()); | |
} | |
m_localDeliverTrace (ipHeader, p, iif); | |
Ptr<IpL4Protocol> protocol = GetProtocol (ipHeader.GetProtocol (), iif); | |
if (protocol != 0) | |
{ | |
// we need to make a copy in the unlikely event we hit the | |
// RX_ENDPOINT_UNREACH codepath | |
Ptr<Packet> copy = p->Copy (); | |
enum IpL4Protocol::RxStatus status = | |
protocol->Receive (p, ipHeader, GetInterface (iif)); | |
switch (status) { | |
case IpL4Protocol::RX_OK: | |
// fall through | |
case IpL4Protocol::RX_ENDPOINT_CLOSED: | |
// fall through | |
case IpL4Protocol::RX_CSUM_FAILED: | |
break; | |
case IpL4Protocol::RX_ENDPOINT_UNREACH: | |
if (ipHeader.GetDestination ().IsBroadcast () == true || | |
ipHeader.GetDestination ().IsMulticast () == true) | |
{ | |
break; // Do not reply to broadcast or multicast | |
} | |
// Another case to suppress ICMP is a subnet-directed broadcast | |
bool subnetDirected = false; | |
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < GetNAddresses (iif); i++) | |
{ | |
Ipv4InterfaceAddress addr = GetAddress (iif, i); | |
if (addr.GetLocal ().CombineMask (addr.GetMask ()) == ipHeader.GetDestination ().CombineMask (addr.GetMask ()) && | |
ipHeader.GetDestination ().IsSubnetDirectedBroadcast (addr.GetMask ())) | |
{ | |
subnetDirected = true; | |
} | |
} | |
if (subnetDirected == false) | |
{ | |
GetIcmp ()->SendDestUnreachPort (ipHeader, copy); | |
} | |
} | |
} | |
} |
其中关键的代码如下:
Ptr<IpL4Protocol> protocol = GetProtocol (ipHeader.GetProtocol (), iif); | |
Ptr<Packet> copy = p->Copy (); | |
enum IpL4Protocol::RxStatus status = protocol->Receive (p, ipHeader, GetInterface (iif)); |
其中的 protocol 就是根据头部协议号决定,这里我们考虑 UDP 协议,那么会执行 UdpL4Protocol 。会执行它的 Receive 方法。
enum IpL4Protocol::RxStatus | |
UdpL4Protocol::Receive (Ptr<Packet> packet, | |
Ipv4Header const &header, | |
Ptr<Ipv4Interface> interface) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << packet << header); | |
UdpHeader udpHeader; | |
if(Node::ChecksumEnabled ()) | |
{ | |
udpHeader.EnableChecksums (); | |
} | |
udpHeader.InitializeChecksum (header.GetSource (), header.GetDestination (), PROT_NUMBER); | |
// We only peek at the header for now (instead of removing it) so that it will be intact | |
// if we have to pass it to a IPv6 endpoint via: | |
// | |
// UdpL4Protocol::Receive (Ptr<Packet> packet, Ipv6Address &src, Ipv6Address &dst, ...) | |
packet->PeekHeader (udpHeader); | |
if(!udpHeader.IsChecksumOk ()) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_INFO ("Bad checksum : dropping packet!"); | |
return IpL4Protocol::RX_CSUM_FAILED; | |
} | |
NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Looking up dst " << header.GetDestination () << " port " << udpHeader.GetDestinationPort ()); | |
Ipv4EndPointDemux::EndPoints endPoints = | |
m_endPoints->Lookup (header.GetDestination (), udpHeader.GetDestinationPort (), | |
header.GetSource (), udpHeader.GetSourcePort (), interface); | |
if (endPoints.empty ()) | |
{ | |
if (this->GetObject<Ipv6L3Protocol> () != 0) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC (" No Ipv4 endpoints matched on UdpL4Protocol, trying Ipv6 "<<this); | |
Ptr<Ipv6Interface> fakeInterface; | |
Ipv6Header ipv6Header; | |
Ipv6Address src = Ipv6Address::MakeIpv4MappedAddress (header.GetSource ()); | |
Ipv6Address dst = Ipv6Address::MakeIpv4MappedAddress (header.GetDestination ()); | |
ipv6Header.SetSourceAddress (src); | |
ipv6Header.SetDestinationAddress (dst); | |
return (this->Receive (packet, ipv6Header, fakeInterface)); | |
} | |
NS_LOG_LOGIC ("RX_ENDPOINT_UNREACH"); | |
return IpL4Protocol::RX_ENDPOINT_UNREACH; | |
} | |
packet->RemoveHeader(udpHeader); | |
for (Ipv4EndPointDemux::EndPointsI endPoint = endPoints.begin (); | |
endPoint != endPoints.end (); endPoint++) | |
{ | |
(*endPoint)->ForwardUp (packet->Copy (), header, udpHeader.GetSourcePort (), | |
interface); | |
} | |
return IpL4Protocol::RX_OK; | |
} |
其中就会执行 (*endPoint)->ForwardUp 。
void | |
Ipv4EndPoint::ForwardUp (Ptr<Packet> p, const Ipv4Header& header, uint16_t sport, | |
Ptr<Ipv4Interface> incomingInterface) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << p << &header << sport << incomingInterface); | |
if (!m_rxCallback.IsNull ()) | |
{ | |
m_rxCallback (p, header, sport, incomingInterface); | |
} | |
} |
这里又是一个回调,其定义如下:
int | |
UdpSocketImpl::FinishBind (void) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this); | |
bool done = false; | |
if (m_endPoint != 0) | |
{ | |
m_endPoint->SetRxCallback (MakeCallback (&UdpSocketImpl::ForwardUp, Ptr<UdpSocketImpl> (this))); | |
m_endPoint->SetIcmpCallback (MakeCallback (&UdpSocketImpl::ForwardIcmp, Ptr<UdpSocketImpl> (this))); | |
m_endPoint->SetDestroyCallback (MakeCallback (&UdpSocketImpl::Destroy, Ptr<UdpSocketImpl> (this))); | |
done = true; | |
} | |
if (m_endPoint6 != 0) | |
{ | |
m_endPoint6->SetRxCallback (MakeCallback (&UdpSocketImpl::ForwardUp6, Ptr<UdpSocketImpl> (this))); | |
m_endPoint6->SetIcmpCallback (MakeCallback (&UdpSocketImpl::ForwardIcmp6, Ptr<UdpSocketImpl> (this))); | |
m_endPoint6->SetDestroyCallback (MakeCallback (&UdpSocketImpl::Destroy6, Ptr<UdpSocketImpl> (this))); | |
done = true; | |
} | |
if (done) | |
{ | |
return 0; | |
} | |
return -1; | |
} |
m_rxCallback 也就是调用 UdpSocketImpl::ForwardUp :
void | |
UdpSocketImpl::ForwardUp (Ptr<Packet> packet, Ipv4Header header, uint16_t port, | |
Ptr<Ipv4Interface> incomingInterface) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << packet << header << port); | |
if (m_shutdownRecv) | |
{ | |
return; | |
} | |
// Should check via getsockopt ().. | |
if (IsRecvPktInfo ()) | |
{ | |
Ipv4PacketInfoTag tag; | |
packet->RemovePacketTag (tag); | |
tag.SetRecvIf (incomingInterface->GetDevice ()->GetIfIndex ()); | |
packet->AddPacketTag (tag); | |
} | |
//Check only version 4 options | |
if (IsIpRecvTos ()) | |
{ | |
SocketIpTosTag ipTosTag; | |
ipTosTag.SetTos (header.GetTos ()); | |
packet->AddPacketTag (ipTosTag); | |
} | |
if (IsIpRecvTtl ()) | |
{ | |
SocketIpTtlTag ipTtlTag; | |
ipTtlTag.SetTtl (header.GetTtl ()); | |
packet->AddPacketTag (ipTtlTag); | |
} | |
// in case the packet still has a priority tag attached, remove it | |
SocketPriorityTag priorityTag; | |
packet->RemovePacketTag (priorityTag); | |
if ((m_rxAvailable + packet->GetSize ()) <= m_rcvBufSize) | |
{ | |
Address address = InetSocketAddress (header.GetSource (), port); | |
m_deliveryQueue.push (std::make_pair (packet, address)); | |
m_rxAvailable += packet->GetSize (); | |
NotifyDataRecv (); | |
} | |
else | |
{ | |
// In general, this case should not occur unless the | |
// receiving application reads data from this socket slowly | |
// in comparison to the arrival rate | |
// | |
// drop and trace packet | |
NS_LOG_WARN ("No receive buffer space available. Drop."); | |
m_dropTrace (packet); | |
} | |
} |
然后调用 NotifyDataRecv 来实现到上层的数据传递
void | |
Socket::NotifyDataRecv (void) | |
{ | |
NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this); | |
if (!m_receivedData.IsNull ()) | |
{ | |
m_receivedData (this); | |
} | |
} |
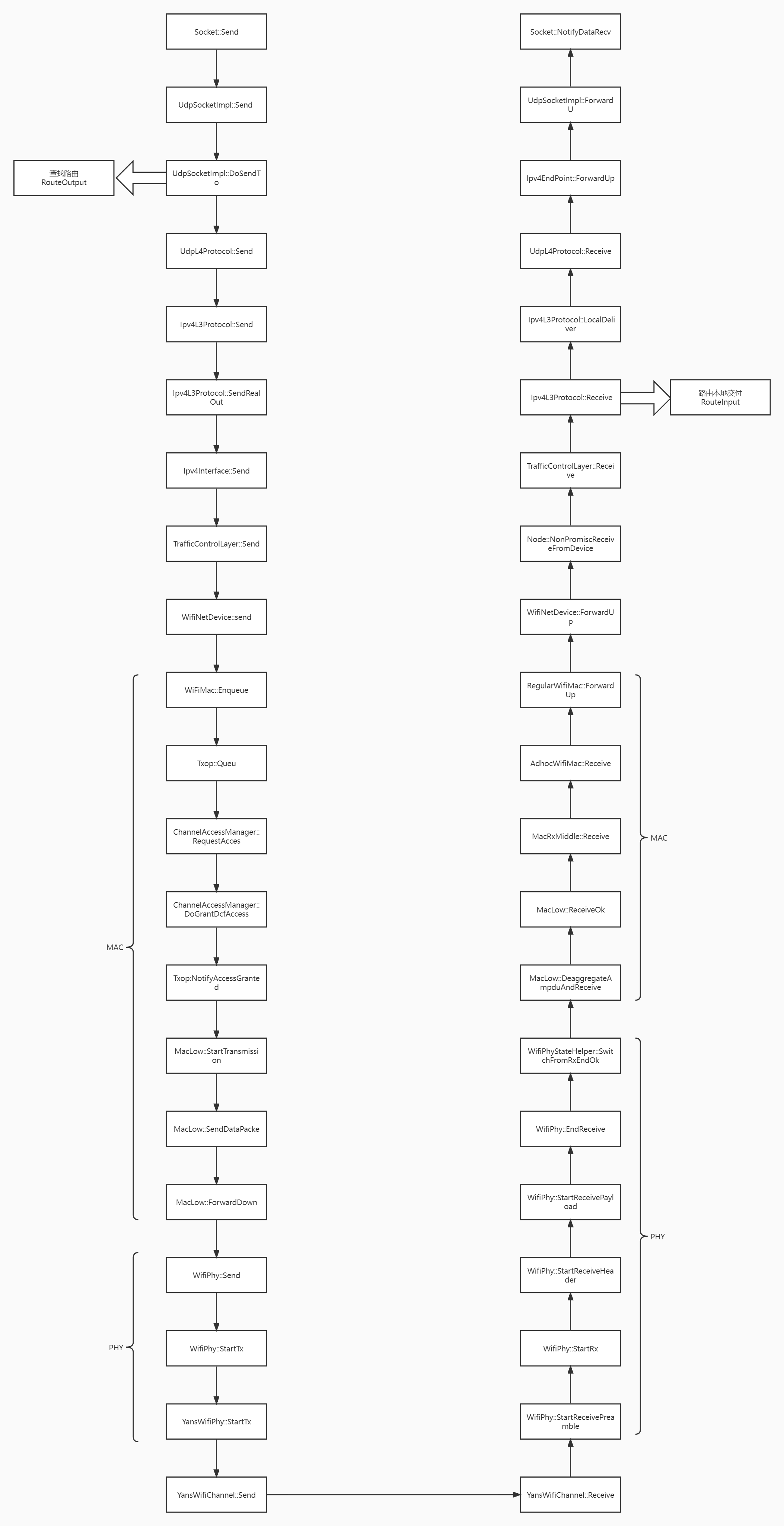
# 完整流程图示意